Software Used on this Project
Project Overview
The Aquatics Centre in Saint-Denis, built for the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic Games, is a multi-award-winning marvel. Designed by schlaich bergermann partner (sbp) in collaboration with architects VenhoevenCS and Ateliers 2/3/4/, and realised by Bouygues Bâtiment (general contractor) and Mathis (Timber sub-contractor) for the Métropole du Grand Paris (client), this facility stands out for its innovative design and engineering. Engineers at sbp used Oasys GSA and the Grasshopper plugin to ensure the building’s structural integrity. As one of the largest timber sports complexes globally, it holds the world record for the largest span of tensioned timber structures. This centre is a prime example of sustainable and lightweight construction in modern sports architecture.
The Aquatics Centre has received numerous accolades, including: Le Grand Prix National de l’Ingénierie 2021; Le Grand Prix du Grand Paris 2023; Grand Prix BIM d’Or 2023; Technical Achievement – Construction Bois 2024 Regional competition; Prix Versailles – World’s most beautiful sports venues list 2024; Structural Awards 2024; Special Prize – FIBOIS France 2024. This impressive list of awards highlights the centre’s excellence in design, sustainability, and innovation.
Covering nearly 10,000 m², the venue features a striking, wide-span suspended timber roof equipped with photovoltaic panels. The roof design carefully aligns with the required dimensions and clearances above the pools, seating areas, and diving platform. Its catenary shape not only enhances the aesthetic but also maximises material efficiency.
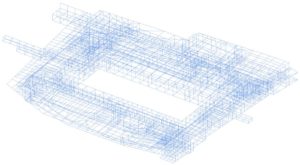
© sbp – model substructure and roof structure
The exposed structural elements throughout the arena are made of timber, capable of supporting loads up to 800 tons. Additionally, the curved, concave roof shape helps to reduce the building’s volume and thus reduces energy consumption for heating.
How Oasys proved invaluable
A key design consideration was the project’s sustainability goals. A minimum of 24kg/m² of bio-sourced material was used (69kg/m² obtained). The lightweight timber (2800m³) tensile form was chosen to minimise the structural material in the roof, alongside low carbon concrete (35%). The customised concave geometry of the roof closely matches the required usable area of the indoor swimming pool to reduce the volume of the hall, leading to corresponding energy savings for heating a smaller space with a reduction of up to 25%. The building length was reduced by choosing one single 70m pool instead of multiple pools separated by a pool deck. The roof is covered with 4,680 m² of photovoltaic panels; one of the largest urban solar farms in France, which covers 25% of the aquatic centre’s electricity needs.
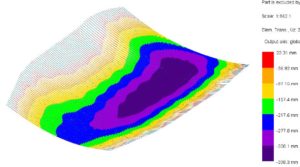
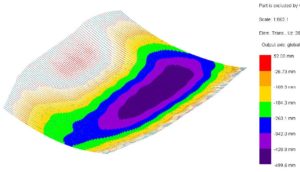
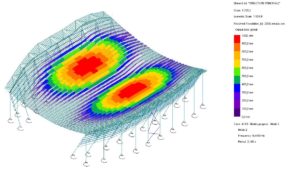
© sbp – vertical deformation of the roof
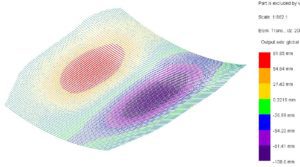
One of the characteristics of a curved, concave geometry is that it requires non-linear second-order calculation in which large displacements must be considered. Suspended structures are very efficient, and the force progression can be easily understood. However, they react sensitively to boundary conditions such as support stiffness, detailing and asymmetrical loads. The deformations are very large, both under gravitational loads and in the opposite direction under wind suction. This can lead to considerable effects on the design.
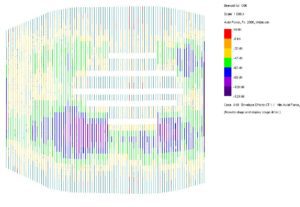
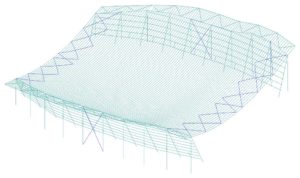
© sbp – roof structure: traction and compression
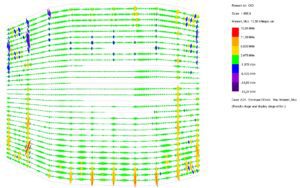
Numerous sensitivity tests with various boundary parameters and their effects on the structural behaviour were investigated. Among other analyses, the following parameters were tested using Oasys GSA and accordingly integrated in the design:
- Concrete base (extension of the column/tension elements)
- Stiffness of the pile foundations
- Spring stiffness of the connections at the base and top of the column
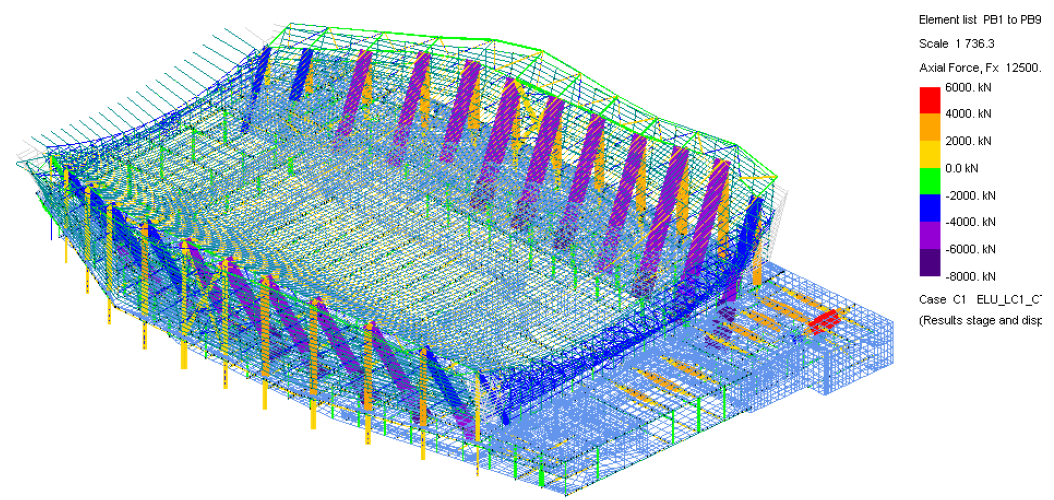
© sbp – sensitivity studies global model
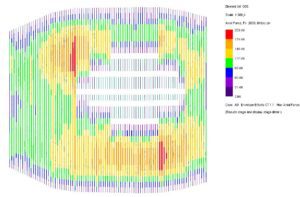
The engineers took advantage of the advanced capabilities provided by the GSA Grasshopper plugin. The seamless integration between the software allowed for optimised calculation times and easy adjustments of various parameters for sensitivity studies.
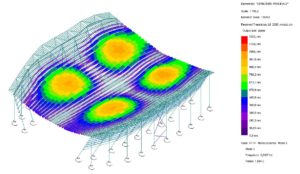
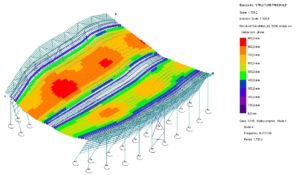
© sbp – principal structure
The use of GSA significantly enhanced the efficiency and collaboration of the structural workflow. The software’s advanced capabilities led to a substantial gain in calculation time, allowing the team to focus on refining the design. Additionally, the fluent exchange with architects facilitated by GSA ensured seamless communication and coordination, which was crucial for the project’s success. The ability to easily adapt geometric parameters enabled the team to conduct thorough sensitivity studies, ensuring the final design was both robust and optimised for performance.
We’d like to thank Managing Director, Michael Zimmermann and Associate Director, Andreas Pfadler at sbp for sharing this work with us.
Read more about the project.
You can find more information about Oasys GSA on the product page or get in touch at [email protected] to discuss our offerings with a member of the team. Interested in the GSA-Grasshopper plugin? Register your interest here.
Photography by Jad Sylla