Software Used on this Project
Project Overview
The Mamu Rainforest Canopy Walkway is a unique tourist facility set on the edge of the Wooroonooran National Park, part of the World Heritage Wet Tropics of Far North Queensland, Australia. The project was sponsored by the Queensland Environmental Protection Agency. Arup were engaged to provide civil, structural, and environmental engineering services for the project.
The project boasts three feature structures; a 370 metre long elevated walkway through the rainforest, a 40 metre high canopy viewing tower, and an 8 metre long cantilever tower. In addition, the project has over 1km of ground level walkway through the rainforest, a bus and car park, a modern office, amenities and ticketing facilities, plus a number of shelters that form interpretative nodes.
How Oasys proved invaluable
Project Design – Feature Structures
The environmental conditions and physical constraints associated with the project site drove the decision to build the structures in hot-dipped galvanised steel, supported on reinforced concrete bored piers and pad footings.
The Arup engineers used GSA extensively in the design of the feature structures. Due to the geometric complexity of the structures, they developed a series of 3-D framework models within GSA to analyse distinct components of the elevated walkway including the main and cantilever towers and the link bridges.
For each of the models, GSA was used to evaluate member design to the ultimate (strength) limit state, and to predict the behaviour of the structures under the serviceability limit states. Cyclonic wind loading formed a significant design criterion for the structures. GSA enabled the design team to accurately model wind loads from a variety of directions, and to evaluate their effect on the structures.
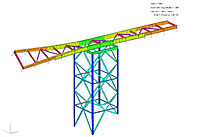
GSA Model
Additionally, GSA output was used in the design of the footing systems for each of the feature structures. For each of the tower models, the software enabled the design team to determine the reactions at the base of each tower leg under the various combinations of permanent, imposed and wind load. They then used these to design an appropriate system of pad footings and bored piers for the feature structures.
In the case of the cantilever tower, GSA was used to evaluate the dynamic behaviour of the structure and to predict the natural frequency of the tower’s first and second modes of vibration. Normally the engineers would want to restrict the structural footfall vibration, but in this instance, the client wanted a “lively” structure to make using the walkway more exciting.
Conclusion
The use of GSA enabled the Arup design team to complete the structural analysis and design of the elevated walkway, main tower and cantilever tower with confidence and efficiency.
By using the advanced features of GSA, Arup were able to deliver a project that provides both client satisfaction and enhances the visitor’s rainforest experience.
The Mamu Rainforest Canopy Walkway