Software Used on this Project
Project Overview
Webb Yates Engineers have used Oasys GSA to design a roof truss for a stadium that cantilevers approximately 29 meters with a 13.7-meter back span. During the project, the engineers were looking at ways to reduce the embodied carbon of the structure despite the roof geometry having already been defined. Structurally, the same truss was repeated throughout the whole stadium, therefore any material savings that were made on any one specific element would be multiplied across the entire project.
How Oasys proved invaluable
The use of GSA in this project ultimately saved the engineers time and allowed them to proceed with ease. A parametric model of the truss was created which allowed the engineers to change the geometry and section properties of the truss members quickly and easily. They used the GSA plugin in Grasshopper to take advantage of the ‘live’ result output that updated when changes to the variables were made. This eliminated the need to export geometry to another piece of software for analysis with each alteration, saving a considerable amount of time.
When using the GSA plugin, the analysis is kept within the Grasshopper script, which allowed the engineers to use the Galapagos Solver. Through adding variables such as truss divisions and section sizes as ‘Genomes’ within the solver, the engineers were able to iterate through many more truss arrangements than they would have been able to if they did not have the GSA plugin.
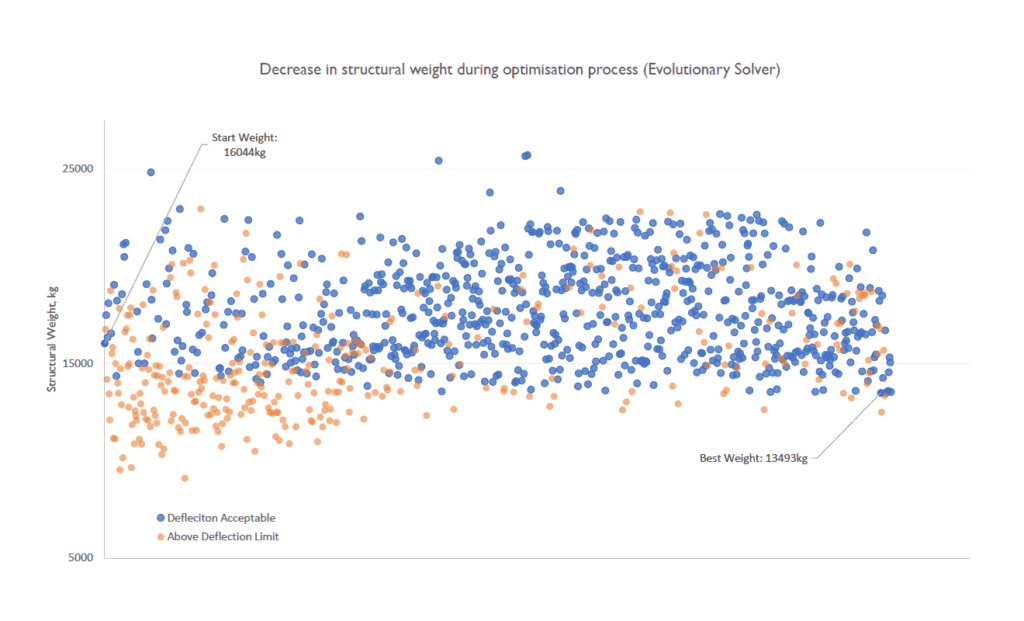
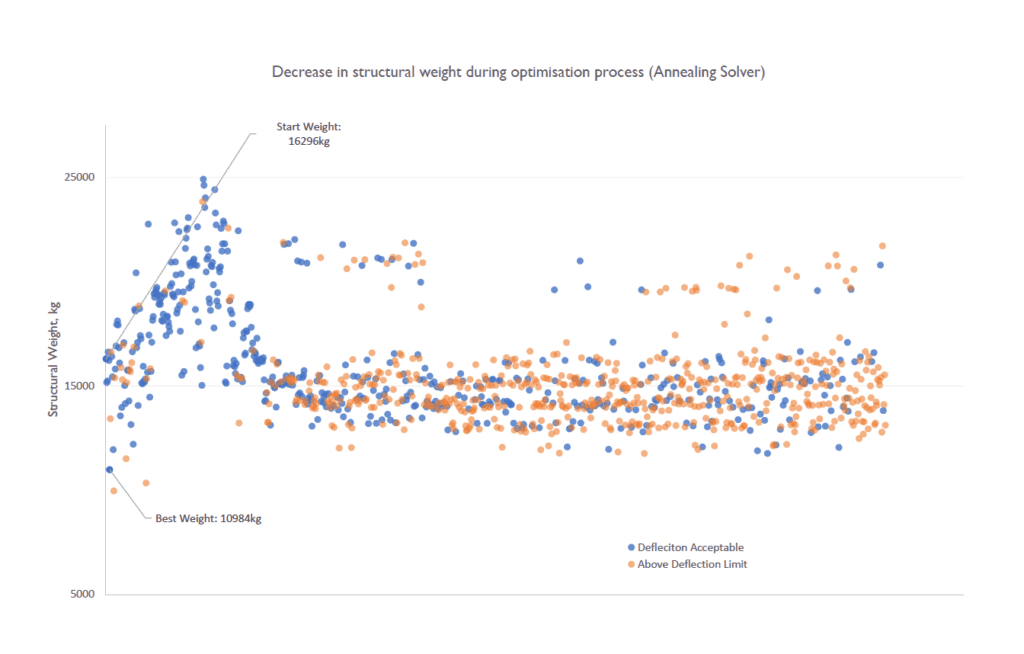
The optimisation process allowed the engineers to find the truss arrangement that had the least weight (and thus, embodied carbon) for a set of design constraints, including a deflection limit. Initial test runs of the optimisation solvers indicated weight reduction of up to 30%, as is shown in the post optimisation model below as it resulted in a more efficient structural arrangement. The engineers are looking to refine the settings to take these findings further.
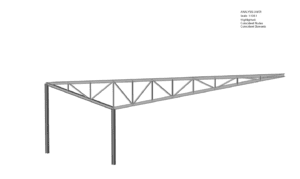
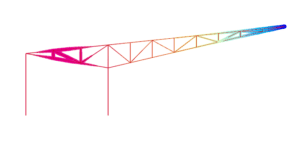
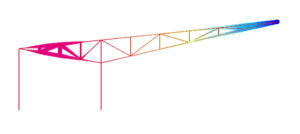
Pre-optimisation Post optimisation
The images above show a contour plot of deflection. The pre-optimisation image shows the geometry and sections used in the beginning, with 22 steel members. The post optimisation image shows the improved geometry (containing 20 members – two less and better positioned to carry the loads) and sections sizes that resulted in the lowest weight.
The use of GSA enabled for an efficient design and analysis process for this project. The engineers were able to interrogate a far greater number of design options swiftly and simply than what would have been possible without the plugin. The GSA Grasshopper plugin allows for both parametric optimisations running GSA headless within Grasshopper, as well as allowing engineers to open existing files to automate their post processing routines. The plugin is available for free but will require GSA10.1 to be installed on your machine to run any analysis tasks. The plugin can be installed directly from within Rhino through Package Manager.
Oasys would like to thank Webb Yates Engineers for sharing this work with us.
Webb Yates Engineers is an award winning structural, civil, and building services engineering design practice with offices in London and Birmingham. They offer a collaborative, enthusiastic and responsive service with an efficient, innovative, and creative design approach.
Find out more about Oasys GSA’s features and capabilities here.